青少年是药物滥用的高危和高发人群。有青春期毒品滥用史的患者,成年期易出现焦虑、冲动和偏执等人格特征,甚至引发犯罪。关晓伟课题组前期研究发现,青春期暴露于可卡因,能够引起内侧前额叶皮层(Medial prefrontal cortex,mPFC)微环境和突触结构的持续损伤,这些适应性变化可能是参与成年后的易焦虑、抑郁等异常精神行为的神经物质基础。
2019年4月,The FASEB Journal在线发表南京中医药大学医学与生命科学学院关晓伟教授课题组的最新研究成果(原文DOI:10.1096/fj.201802192RR):青春期可卡因暴露史可增强前边缘皮层(Prelimbic cortex,PrL)的GABA能中间神经元——锥体神经元的局部神经通路的投射活动,导致锥体神经元的E/I(兴奋/抑制)失衡,进而引发成年期出现的焦虑样与抑郁样行为。该研究发现,青春期可卡因暴露的小鼠,成年脑中PrL第V层锥体神经元的活性降低、对称性突触的比例增加;同时,这些锥体神经元的mIPSC显著增强,伴随PrL脑区的GABA水平的增加;PrL脑区GABA能系统的分子信号也同步发生改变。该项研究将有助于揭示青少年药物滥用对脑功能的长期影响及其神经生物学机制,为针对青少年吸毒患者的“个体化”戒毒治疗的新药开发提供新的思路和神经靶标。
该项研究由南京中医药大学医学与生命科学学院关晓伟教授课题组与上海精神卫生中心袁逖飞教授课题组合作完成,葛菲菲副教授为共同通讯作者。
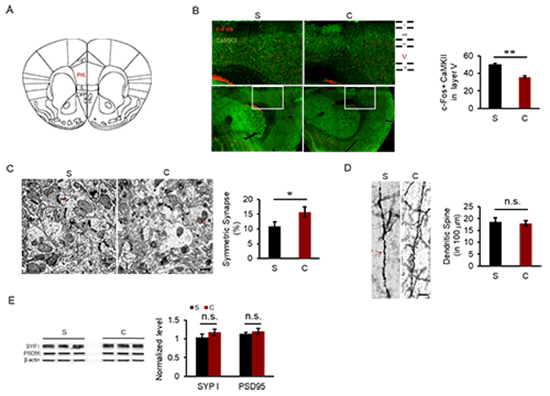
Figure 1. Neural activity and synapse in PrL. A, Illustration of PrL region. B, Activities of pyramidal neurons at layer V of PrL. In the left picture, red colored staining indicates c-Fos positive cells, and green CaMKII-labeled staining shows pyramidal neurons. C, Synapse of PrL by TEM. Arrow head indicated asymmetrical synapse, while arrows indicated symmetrical synapses. Scale bar: 500 nm. D. Density of dentritic spine at layer V of PrL by Golgi staining. Arrows indicated dendritic spines. Scale bar: 6 μm. E, Expression of synapse-related proteins, including SYP I and PSD95.
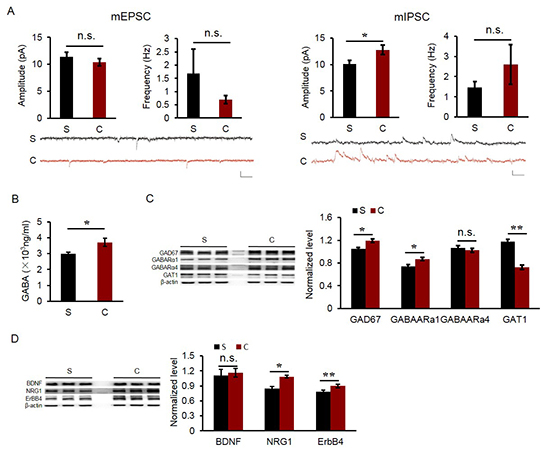
Figure 2. Electrophysiological tests and molecules of GABAergic system in adult PrL. A, mEPSP (left) and mIPSC (right) of pyramidal neurons at the layer V of adult PrL. B, Concentration of GABA in adult PrL. C, Levels of molecules in GABAergic system. Levels of GAD67, GABAAα1, GABAAα4 and GAT1 were detected in adult PrL. D, Regulatory molecules to GABAergic transmission. Levels of BDNF, NRG1 and ErbB4 were examined in adult PrL.
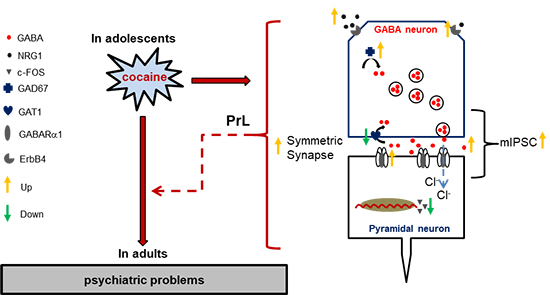
Figure 3. Proposed model of the present study. Adolescent cocaine exposure often increases the risk of psychiatric disorders persisting into adulthood. In this study, we found that adolescent cocaine exposure enhances GABAergic transmission in adult PrL, as indicated by increased GABA concentration, GAD 67 level, GABA receptor level, symmetric synapses and mIPSC. The increased levels in NRG1/ErbB4 signal pathway might account for the enhancement of inhibitory transmission. The enhanced GABAergic transmission on pyramidal neurons might lead to hypoactivity of PrL, which may contribute to prolonged psychiatric disorders in adulthood.
(供稿部门:人体解剖与组织胚胎学系;供稿人:葛菲菲)
